Arrests reveal debate about costs and benefits of proton therapy
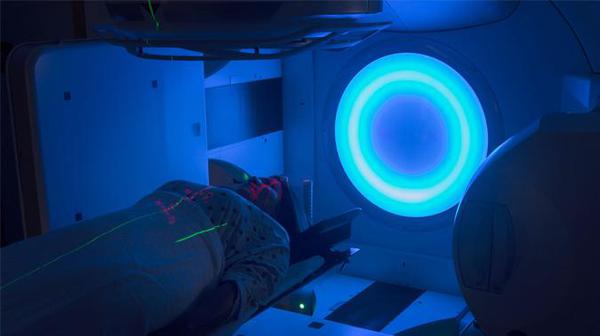
Both proton and standard photon radiation achieve the same goal of damaging tumor cell DNA. But because protons are heavier, they stop at their target, thus reducing extra radiation to noncancerous areas. This is ideal for treating tumors near sensitive structures, such as the brain or spinal cord, or for treating childhood cancers, as radiotherapy comes with a risk of developing secondary cancers decades later.